A Value-Based Model that Drives Real Outcomes in Primary Care
DOWNLOAD AS PDF 30 MIN READ
Welcome to VItalSync Health Health, your trusted partner in revolutionizing primary care delivery.
We’re a Premier Care Management firm dedicated to guiding independent physician practices, health systems, employers, and payors through a seamless transition from the traditional, fragmented fee-for-service model to a cutting-edge, value-based care approach.
Redefining primary care: VitalSync Health's model prioritizes patients, employing a team-based approach anchored by physicians. Includes care management, navigation, community health workers, population health, and clinical pharmacy.

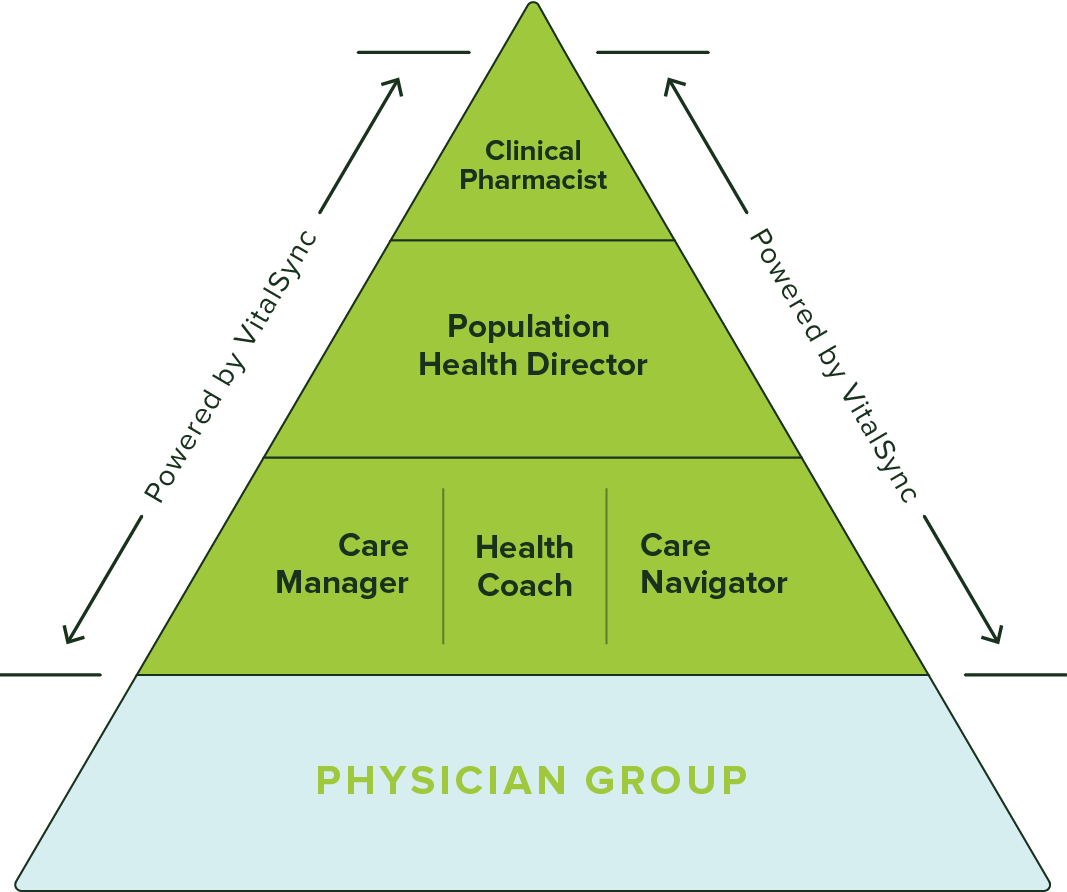
Committed partners strive for TRIPLE AIM: improve patient outcomes, employ effective population strategies, and reduce care costs. Our innovative model extends Primary Care nationally, enabling groups to transform healthcare and reshape the primary care paradigm.
Advanced Primary Care is a health care delivery model that prioritizes strong relationships between patients and their doctors with additional support from data, analytics and coordinated care.

APC is a practice that shifts the focus of primary care toward quality. Instead of focusing on numbers, APC ensures patients are provided with high-quality care.
APC frees healthcare providers from traditional time constraints by reducing the necessity to see a large number of patients. The impact of advanced primary care is crucial for patients dealing with the intricacies of healthcare.

The following five capabilities play a crucial role in the model’s ability to deliver improved health outcomes at a lower cost. Let’s take a deeper look:
We extend your practice’s capabilities by integrating a state-of-the-art, team-based approach.
Navigating patient care with a tailored approach.
Ensuring the provision of quality care, addressing chronic conditions, implementing remote patient monitoring, annual wellness visits, integrating behavioral health, and fostering overall well-being. All these efforts are orchestrated collaboratively among the care team, creating a seamless and patient-centered experience.
Primary care providers often act as a conduit to specialty care, with limited time for in-depth diagnosis. Our approach emphasizes direct, comprehensive diagnosis to prevent unnecessary referrals and ensure that treatment addresses
the true health issues.
RPM employs digital tools to capture and send patient health data remotely, using devices like wearables and blood pressure monitors for real-time assessments. The aim is to improve care access, patient outcomes, and cost efficiency.
CCM offers a holistic care strategy for chronic diseases, integrating medical, lifestyle, and psychological support to enhance patient life quality, prevent disease progression, and encourage self-care.
BHI merges mental and medical care within primary settings, fostering comprehensive treatment plans for mental health and substance disorders, aiming for a whole-person care approach that enhances patient outcomes and reduces costs.
An “extra hand” that works with the care manager to Identify and address Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) and guiding patients through insurance and healthcare navigation. Care navigation is apatient-centered approach aimed at assisting individuals in accessing and coordinating healthcare services efficiently and effectively. It involves guiding patients through the complexities of the healthcare system, helping them overcome barriers to care, and empowering them to make informed decisions about their health.
Here are 4 ways care navigation contributes to value-based care:
By providing personalized support and guidance, care navigation helps patients better manage their health conditions, adhere to treatment plans, and access appropriate services in a timely manner. This can lead to better health outcomes and reduced hospital readmissions.
Care navigation facilitates smoother transitions between different healthcare settings and providers, reducing confusion and frustration for patients. By offering support tailored to individual needs, it improves patient satisfaction and engagement in their care.
Effective care navigation can help prevent unnecessary hospitalizations, emergency room visits, and duplicative tests or treatments. By promoting proactive management of health conditions and appropriate utilization of resources, it contributes to cost containment and efficiency within the healthcare system.
Care navigation includes education and support for preventive measures, such as screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle modifications. By promoting proactive healthcare management and early intervention, it contributes to population health improvement and supports the shift towards preventive and wellness-focused care models.
Population Health Directors: Utilizing proactive data analytics to identify and triage at-risk patients. Population health management is a proactive approach to improving the health outcomes of a defined group or population. It involves analyzing health data, identifying health needs and disparities, implementing interventions to address those needs, and measuring outcomes to continuously improve care delivery and health outcomes at the population level.
Every population can be broken down into three general segments:
Population health management enables the identification of high-risk individuals or subpopulations based on factors such as chronic conditions, socio-economic status, and health behaviors. By stratifying the population according to risk, healthcare organizations can target interventions and resources where they are most needed, such as care coordination for high-risk patients or preventive services for at-risk populations.
Population health management relies on data analytics and performance metrics to inform decision making, monitor progress, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. By leveraging data from electronic health records, claims data, and other sources, healthcare organizations can identify areas for improvement, measure the impact of interventions on outcomes and costs, and continuously refine their population health strategies to achieve better value for patients and stakeholders.
Community health work involves engaging with individuals and communities to promote health, prevent disease, and address health disparities. These workers are often from the communities they serve, which allows for culturally sensitive and tailored approaches to health promotion and education.
Here are 4 ways community health workers contribute to value-based care:
Community health workers serve as trusted liaisons between healthcare providers and underserved populations. By building relationships and trust within their communities, they help individuals overcome barriers to accessing healthcare services, such as language barriers, cultural differences, transportation issues, and lack of health insurance. This improves access to care and reduces disparities in health outcomes.
Community health workers provide health education and promote healthy behaviors within their communities. They deliver information on topics such as preventive care, nutrition, exercise, chronic disease management, and maternal and child health. By empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and adopt healthier lifestyles, they contribute to disease prevention and improved health outcomes.
Community health workers provide personalized support in navigating the healthcare system, aiding understanding of treatment plans, navigating complex healthcare processes, and accessing social services. Addressing social determinants like housing, food insecurity, and transportation, they enhance care coordination, ensuring continuity and supporting patients for improved health outcomes.
Community health workers, often from the served communities, possess cultural competence and language skills, fostering trust crucial for patient engagement, treatment adherence, and behavior change. By overcoming cultural and linguistic barriers, they facilitate effective communication, contributing to patient-centered care delivery and positive health outcomes.
With 80% of chronic conditions managed through therapeutics, it makes sense to have a pharmacist on the care team, optimizing medication therapy and overseeing drug interactions. Clinical pharmacy is a specialized field of pharmacy practice that focuses on the direct provision of patient care, collaborating with healthcare providers to optimize medication therapy outcomes. Clinical pharmacists work closely with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure safe, effective, and appropriate medication use for individual patients.
Here are 3 ways clinical pharmacists contribute to value-based care:
Clinical pharmacists conduct comprehensive medication reviews and assessments to identify potential medication-related problems, such as drug interactions, adverse effects, and inappropriate dosing. By optimizing medication therapy regimens and promoting adherence, they improve patient outcomes, reduce medication errors, and prevent adverse drug events, ultimately leading to better value in healthcare delivery.
Clinical pharmacists collaborate with healthcare teams to select the most appropriate and cost-effective medications for patients based on their clinical needs, preferences, and insurance coverage. They help minimize medication costs by identifying therapeutic alternatives, optimizing drug dosing, and implementing evidence-based prescribing practices. By promoting the use of generic medications and advocating for medication affordability, clinical pharmacists contribute to cost containment and value-based decision making in healthcare.
Clinical pharmacists play a crucial role in managing chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. They provide patient education and counseling on medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and self-management techniques. By monitoring patients’ progress, adjusting medication regimens as needed, and identifying barriers to adherence, they help patients achieve better control of their chronic conditions, reduce complications, and improve quality of life, thereby enhancing the value of care delivery.
True APC is a model where everyone wins: providers, patients, payers, and employers.
APC isn’t just a model that works for patients and payers. It is also a model for those who deliver care. There are three main reasons for this dynamic:
Providers under the APC model shift from volume-based to value-based care delivery, where incentives are aligned with the quality of patient care rather than the quantity of procedures performed. This shift allows providers to spend more meaningful time with each patient, fostering a deeper understanding of their health needs and delivering more personalized care.
Because APC focuses on providing a large portion of care in the primary care setting, APC empowers providers to fully utilize their training and skills, elevating their role beyond mere gatekeepers to specialists. Providers become an even more central figure in their patients’ health journeys, offering comprehensive care that can lead to improved health outcomes and patient satisfaction.
In addition to having more time with patients and the incentive to provide whole health care, providers in the APC model benefit from the additional support of an extensive care team. This includes Community Health Workers and Health coaches who work with patients on behavior change and allied health professionals who assist with complex cases. The collaboration within these teams allows for a holistic approach to health, addressing both physical and behavioral health needs comprehensively.
In the APC model, financial incentives are provided for the quality of care provided, not just reimbursement for procedures. As a result, a provider can expect to generate net new revenue from the enhanced care provided by the APC extended team.
Payers looking to build a competitive advantage in their markets set themselves apart from their competitors in five specific ways when they implement APC:
The APC model is designed to move beyond mere symptom treatment. Providers have the time and resources to explore the underlying causes of health issues, including physical symptoms and social determinants that impact health. This comprehensive view enables the development of tailored care plans that address patients’ overall well-being.
When APC is backed by employers or included in payer health plans, patients typically face reduced or no direct costs. This is significant for those who might otherwise neglect their health due to financial concerns, helping to prevent the deferment of necessary care due to prohibitive costs.
The model facilitates a healthcare experience that balances the necessity for a healthy lifestyle with financial sustainability. This personalized approach has always been a hallmark of care within the APC model, ensuring patients receive the support they need without financial strain.
By offering comprehensive, coordinated healthcare services, patients enjoy a more seamless and convenient care journey, which contributes to their overall satisfaction with the healthcare system.
APC models typically emphasize patient education and empowerment, providing patients with the knowledge to make informed health decisions, further enhancing satisfaction.
Payers looking to build a competitive advantage in their markets set themselves apart from their competitors in five specific ways when they implement APC:
By providing the majority of care within the primary care setting, APC acts as a comprehensive healthcare hub. This not only simplifies care delivery but also allows for the integration of data analytics, virtual care, and health coaching, which can lead to better health outcomes for larger populations while simultaneously controlling costs.
Payers can address the shortage of primary care by integrating dedicated access into health plans, which can significantly enhance member access to care. Removing physical, financial, and cultural barriers increases primary care utilization and member satisfaction.
For payers with Medicare Advantage members, APC can improve key performance indicators, such as HEDIS scores and star ratings, which can lead to financial benefits from CMS incentives and reductions in the total cost of care.
With APC, longer appointments and empathetic listening become the standard, providing members with the opportunity to address their health concerns comprehensively. This leads to a better care experience where members feel genuinely heard, often for the first time.
By adopting the APC model, payers set themselves apart in a competitive marketplace. The comprehensive care, preventive focus, and improved member access serve as distinguishing features that can attract new members and retain existing ones. The integration of APC can showcase a payer’s commitment to innovation and member-centric healthcare, creating a unique selling proposition in the healthcare insurance landscape.
Self-insured employers get four key benefits from APC:
Employers partnering with APC providers can assert more control over their healthcare benefits, leading to more predictable healthcare spending and lower overall costs. This is crucial for avoiding the traditional cycle of rising healthcare costs and the difficult choice between cutting benefits or shifting costs to employees.
Healthier employees are more engaged and productive. The APC model supports employee health through preventive care and wellness programs, which leads to reduced absenteeism and a more dynamic work environment.
Employers can substantially improve the health benefits offered, enhancing health outcomes for their workforce while controlling the rise of benefits costs.
Today’s workers seek out employers who offer more than just a paycheck; they value comprehensive healthcare benefits that focus on holistic health. APC enables employers to meet these expectations, providing a competitive edge in talent acquisition and retention.
The landscape of healthcare is evolving rapidly, with Advanced Primary Care (APC) at the forefront of this transformation. Stay ahead of the curve. If you’re interested in learning how the APC model can benefit you and your organization, we’re here to start the conversation. Let’s connect and explore the possibilities together.